Liver Transplant in Iran all You Need to Know
The liver is the largest internal organ of the body. Its weight in an adult is about 3 pounds or 1.4 kilograms.
This organ is located just below the diaphragm on the right side of the abdomen and below the ribs and performs many important functions, such as producing protein and breaking down food nutrients to help the body store the energy it needs.
Almost all the blood in the digestive tract, which is rich in nutrients, passes through the liver.
The nutrients absorbed from the small intestine in the liver are converted into substances that are necessary for life.
The liver also secretes bile, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats, cholesterol, and fat-soluble vitamins.
And thus, this organ plays an effective role in regulating the amount of sugar, fat, protein and processing of nutrients and hormones.
In addition, the liver plays an effective role in storing vitamins and is responsible for the metabolism of most drugs.
It is also responsible for making proteins that help blood clot.
Liver is an effective organ in detoxification and removal of bacteria, prevention of infection and regulation of immune system responses.
Due to the vital role of this organ, its failure is associated with many symptoms.
If the liver, this very important organ, has failed due to various diseases and other treatment methods have been rejected for the disease; The only option left for doctors is a liver transplant.
Because unlike the artificial heart or the dialysis machine that performs the work of the kidney, no artificial device has been made that can perform even a part of the functions of the liver in the body.
Causes of the need for Liver Transplantation Surgery
Liver transplantation procedure is usually considered a treatment option for people who have significant complications due to advanced chronic liver disease.
If the patient has not responded to other treatment methods, the option of organ transplantation is chosen.
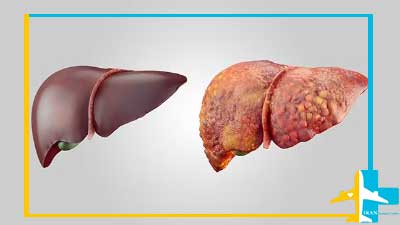
Chronic liver failure may be caused by various diseases. The most common cause of chronic liver failure is liver cirrhosis.
When cirrhosis occurs, scar tissue replaces normal liver tissue and causes the liver to not function properly.
The main causes of cirrhosis leading to liver failure are:
- Liver diseases such as hepatitis B and C.
- Alcoholic liver disease (which causes damage to the liver due to excessive alcohol consumption.)
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (in which fat accumulates in the liver and causes inflammation or damage to liver cells).
- Genetic diseases affecting the liver, including hemochromatosis (which causes excessive accumulation of iron in the liver) and Wilson’s disease (which causes excessive accumulation of copper in the liver).
- Diseases that affect the bile ducts (tubes that carry bile from the liver), such as primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and biliary atresia (which is the most common reason for liver transplant in children).
Also, accidents can lead to severe damage to the liver and its failure.
Some patients with liver cancer whose condition cannot be controlled may also lead to the option of liver surgery.
A liver transplantation may also treat certain cancers that originate in the liver.
Liver donors Candidate
- Deceased donor: People who are brain dead can be a source of liver donation for people in need. In Iran this option is not available for foreigners.
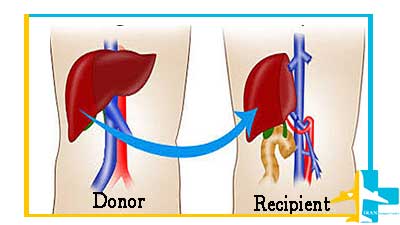
- Living donor and partial liver transplantation from a living person: A person with a healthy liver can donate a part of his liver to others.
Living Donor Liver Transplantation
A living liver donation is an alternative to waiting for a deceased donor liver to become available. Since 1994, liver transplantation has been performed in Iran, and since 1997, has been performed from a living donor.
In living liver donation, a part of a healthy liver from a living person is surgically removed and immediately transplanted to the recipient, and the patient’s liver is completely removed.
The human liver regenerates and returns to its normal size in a short period of time and within a few weeks after the removal of a part of the organ. And both liver donor and recipient can continue their normal life.
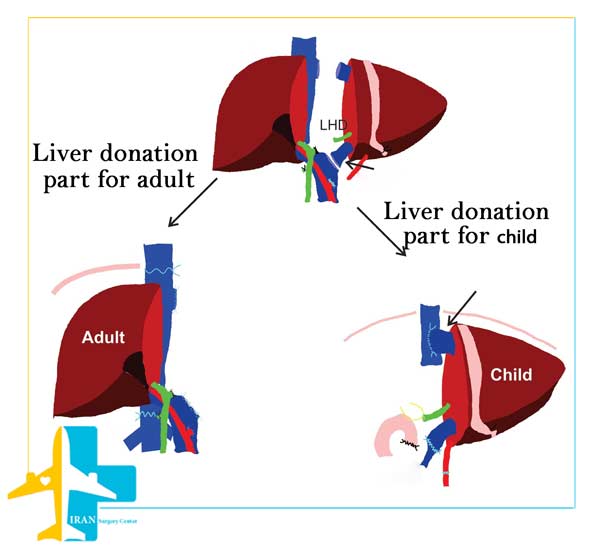
In a Living Donor Liver Transplant, 55 to 70% of the liver (right lobe) is removed from the living and healthy donor.
Sometimes 70% of the donor’s liver can be removed without harming the donor. The transplanted part will be fully functional in the recipient.
Our doctors at Iran surgery center can remove up to 80% of a healthy person’s liver without causing any problems to the donor.
About 20% of the liver is removed from a living donor for children.
It is better for the closeness and genetic compatibility of the donor to be a close relative of the patient.
More than 1,500 people die each year due to organ shortage while waiting for a liver transplant. While most of these people were candidates for receiving a liver from a living donor.
Despite all the advantages, the technique of partial liver transplant with a living donor is more complicated than a transplant from a deceased cadaver.
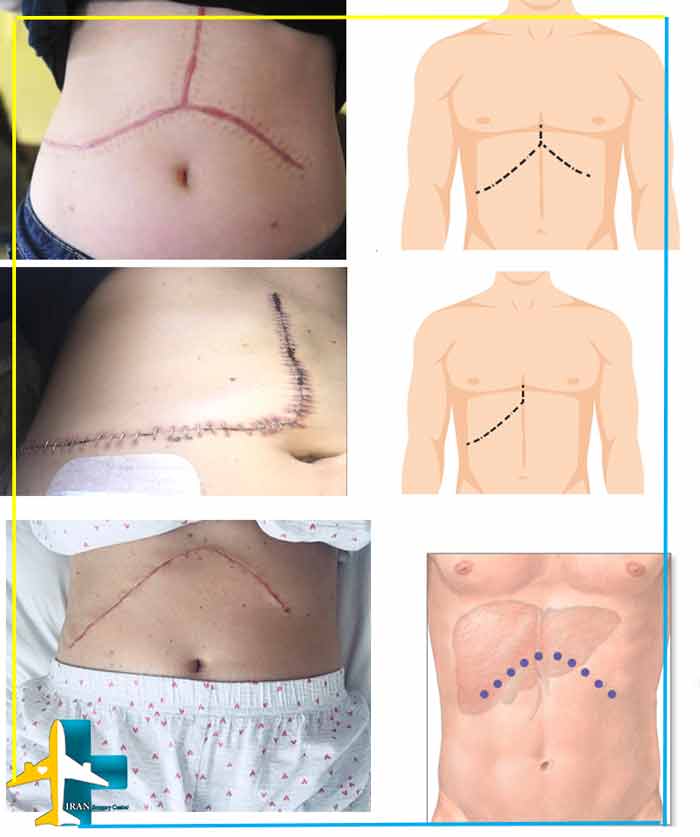
Liver Surgery Scars
Advantages of Living-Donor Liver Transplant
- No waiting to receive a liver
- The ability of the surgeon to properly plan for both the recipient and the donor
- A liver from a living person lives longer than a liver from a corpse.
- Living liver transplantation can be performed electively and before the onset of life-threatening complications.
- Significant regenerative capacities of the human liver
- Widespread shortage of cadaveric livers for patients awaiting transplantation
Liver donor conditions in living liver donation
A suitable donor must have the following conditions:
- Age between 18 and 60 years
- Good physical health without physiological diseases and drug use
- Ability to understand and follow instructions for pre-operative preparation and post-operative recovery
- Having a liver the same size or larger than the recipient
- Performing additional tests to ensure that the transplanted tissue does not return to the body of the liver recipient
- Do not smoke for at least 6 weeks before surgery
- Having a charitable desire to donate without financial incentives
- Sometimes a CT scan and MRI of the liver are also performed.
Precautionary measures before liver transplantation surgery
The special tests, steps and consultations that take place before the surgery are:
- Laboratory tests such as blood and urine tests to assess the health of organs, including the liver
- Types of imaging tests of liver and abdominal organs and blood vessels and lungs
- Heart test and ECG to determine the health of the cardiovascular system
- A general examination, including cancer screening tests, to assess general health and check for other diseases that may affect the outcome of the transplant.
- Endoscopy to access wounds and inflammations of the esophagus and stomach
- ERCP – endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography – to see the bile duct
- Liver angiography image
- Liver sampling
- Psychological assessment in terms of the patient’s full familiarity with the risks and side effects of transplantation
After these tests and consultations are completed, the transplant center meets to discuss the patient’s condition and determine if a transplant is the best treatment option for the patient.
If the answer is positive, the patient will be placed on the waiting list.
Liver-Transplant Waiting List
Doctors use the results of liver function tests and other factors to assess the severity of the disease, to determine how much the patient needs a transplant.
Transplant waiting list priority is determined by two scoring systems called the (MELD) for adults and the Pediatric End-Stage Liver Disease (PELD) system for children younger than 12 years.
The doctor uses a special formula to determine the MELD score, which can range from 6 to 40.
A high MELD score indicates an urgent need for transplantation.
The waiting time in the waiting list is based on the MELD scores and blood group of the person.
And the patient may be hospitalized during this time. If the patient’s condition worsens, his MELD score will change.
If you choose Iran surgery center as the destination for liver transplant, the surgery will be performed in the shortest possible time without waiting.
After arriving in Iran and performing initial tests, the patient care team will admit and examine the patient to ensure that the patient is sufficiently prepared for surgery. Then they start the process of donating a liver from a living donor.
How is Hepatic Transplantation in Iran is performed ?
Liver surgery or hepatic transplantation is performed using general anesthesia and usually takes between 6 and 12 hours. The surgeon makes a long incision across the patient’s abdomen to access the patient’s liver.
The place and size of the incision can be different according to the surgical method and anatomy of the person.
The surgeon removes the patient’s liver and places the donor liver in his body, then the patient’s blood vessels and bile ducts are transplanted to the new liver.
Since this organ transplant is a major surgery, surgeons have to insert multiple tubes into the body.
These tubes are necessary to help the body perform certain functions during surgery and for a few days after.
After transplanting a new liver, the surgeon sutures the surgical incisions and the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for recovery.
If the partial liver transplant involves the removal of the lobe or the part involved in the tumor and the healthy parts of the liver remain, the patient’s recovery time will be much faster and the patient will be under hospital care for only 5 to 7 weeks.
Hospitalization and recovery of hepatic transplantation in the hospital is for 4 weeks to 5 months, depending on the surgical technique and the patient’s condition.

Liver Surgery results in Iran
A person’s chance of a successful liver transplant and long-term survival depends on the specific condition of his body.
Overall, about 75 percent of people who receive a liver transplant, live at least five years. This means that of every 100 people who receive a hepatic transplantation for any reason, about 75 will survive five years and 25 will die within five years.
People who receive a liver from a living donor often have better short-term survival rates than people who receive a liver from a deceased donor.
But long-term outcomes are difficult to compare because people with living donors usually have a shorter wait for a transplant and are not as sick as those who receive a liver from a deceased donor.
Your outlook after surgery depends on many things, including the condition that caused your liver to fail.
About 88% of patients live at least one year, and 73% at least 5 years after transplantation.
Liver Transplant Success Rate in Iran
The success rate of Iranian doctors is on par with the specialists and surgeons of advanced countries, and the 3-year success rate is 85%.
The survival rate of patients after surgery has reached 94%, and the survival rate of hepatic transplant patients has reached 90% in the first year, 80% in the first 5 years, and 71% in ten years.
The one, five and 10-year survival rates for children receiving livers are 76%, 67% and 56%, and we are at the top in the Middle East in terms of liver transplants.
In general, during a period of 20 years, 77.4% of transplanted patients have continued to live, which is considered a unique record for performing liver transplantation during a period of 20 years in the world.
Complications of Liver Transplant Operation for Donor
Living-donor liver transplant have good results, but finding a living donor can be difficult. This surgery also has risks for the donor. including blood clots and bile problems, but these issues are relatively easy to fix.
In various operations, complications in the donor are around 10% and in many cases a second operation is required.
Common complications are biliary fistula, gastric stasis and infection, which are more common after removal of the right lobe of the liver.
Post-donation mortality has been reported to be 0% in Japan, 0.3% in the United States, and <1% in Europe. This risk decreases with increasing experience of surgeons.
In Iran, the risk of death due to donating part of the liver is estimated to be 1 in 500 cases, which means it is about 0.05 and less than 1%.
Complications of Liver Transplantation Surgery for the Recipient
There are risks associated with the procedure itself, as well as complications of medications after surgery.
The immune system attacks and destroys any invaders in the body. But it cannot tell the difference between a transplanted liver and unwanted invaders like viruses and bacteria.
Hence, the immune system may attack the new liver. This process is called graft rejection.
About 64% of organ transplant patients experience organ rejection, most of which occur in the first 90 days. Anti-rejection drugs will be prescribed to prevent an immune attack.
In liver transplantation, three types of rejection may occur, which include the following:
- Super acute rejection: secreted antibodies cause a reaction and usually has a profound effect. This rejection happens at the moment of transplantation or a few hours after the operation.
- Acute rejection: This type of rejection is more common and suppressive drugs are usually prescribed to prevent this type of rejection. This rejection may happen a day or a few weeks after the operation.
- Chronic rejection: This type of rejection occurs without any signs and symptoms about a year after the transplant. The cause of this type of rejection is unknown, but acute rejection is a strong predictor of chronic rejection.
Clinical signs of transplant rejection
Clinical signs of transplant rejection include: encephalopathy (a dysfunction or disease of the brain), jaundice, bruising, and bleeding. Other symptoms include: weakness, anorexia, muscle pain, low fever, a slight increase in white blood cell counts, and sensitivity in the operation area with pain.
According to the organ transplant organization, more than 10% of liver transplants performed worldwide are rejected in the early stages, while the number of hepatic transplantation rejections in Iran is less than 8%.
In addition to transplant rejection, the risks associated with liver surgery include:
- Bile duct complications, including bile duct leakage or narrowing of the bile ducts
- Bleeding and surgical wound infection
- Blood clot:
formation of a clot in the artery that carries blood from the heart to the liver (so-called hepatic artery thrombosis) or in the vein that carries blood from the intestine, pancreas, and spleen to the liver (portal vein thrombosis).
4.Donor liver failure and liver function problems:
About 1% to 5% of new livers do not work as well as they should or at all. If the problem does not improve quickly, a second transplant may be necessary
5.Infection:
Medicines that prevent the body from rejecting the new liver weaken the immune system. These drugs are called immunosuppressants. These increase the chance of infection. This problem will be solved with time.
6.Mental confusion or convulsions
Long-term complications may include recurrence of liver disease in the transplanted liver.
7.Return of the disease
Some diseases such as (hepatitis C, primary sclerosing cholangitis, fatty liver disease) that lead to liver failure can still affect or destroy the new liver.
8.cancer
Organ transplant recipients are 25% more likely to develop skin cancer.
9. Immunosuppressive drugs can also increase the risk of other cancers, including a rare condition called post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD).
10.Side effects of anti-rejection drugs
After the liver transplant, drugs must be used until the end of life to prevent the body from rejecting the donated liver. Sometimes anti-rejection medications may be stopped slowly.
These anti-rejection drugs can cause various side effects, including: bone thinning, diabetes, diarrhea, headaches, high blood pressure, high cholesterol.
We at the Iran Surgery Center, in cooperation with Iran’s first-rate doctors and advanced hospitals, will take all the necessary measures to minimize the complications of surgery and return to a healthy life.
You may not be able to be transplanted if you have any of the following:
- Severe infection
- Diseases caused by alcohol or drug use
- Cancer outside the liver
- Serious heart or lung disease

Lifestyle after Liver Transplant Procedure
Having realistic expectations of transplant outcomes can help reduce stress and help you adapt to new circumstances.
Proper diet
After a liver transplant, it is important to eat a balanced diet to help your liver recover and maintain a healthy liver.
In general, the diet after liver surgery should be low in salt, cholesterol, fat and sugar.
- To prevent damage to the new liver, it is important to avoid alcohol.
- Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice because of their effects on a group of immunosuppressant drugs
- Get enough fiber and choose whole-grain foods instead of processed foods and eat at least five servings of fruits and vegetables a day
- Consumption of dairy products and low-fat or fat-free meats, which are important for maintaining optimal levels of calcium and phosphorus.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and other fluids daily
Exercise and physical activity
Immediately after the liver transplantation, you should walk as much as you can. Then, depending on how your condition progresses, you can incorporate more physical activity into your daily life.
Walking, biking, swimming, low-impact strength training, and other physical activities you enjoy can all be part of a healthy and active lifestyle after a liver transplant.
The Liver Transplant Cost in Iran
Liver transplant cost in Iran surgery center is about 30 thousand dollars, which includes all costs related to surgery like hospital and operating room, tests and examinations before and after the operation, as well as all measures and logistics services, including accommodation, transfer, translator and etc.













My father need a liver transplant. My blood type is o-and his is o+. Can I be a donor for him?
yes its ok